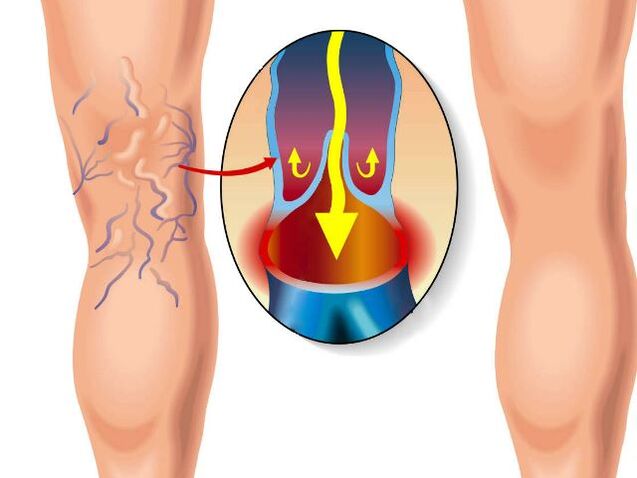
Varicose veins in the lower legs are considered the most common peripheral duct pathology, it is one of the ten diseases of civilization mentioned. According to epidemiological studies, venous insufficiency occurs in 80% of people of working age. In most cases, varicose veins on the legs do not cause serious suffering, and sometimes are not known at all, do not require treatment. Even so, there are situations where it is necessary, without delay, to see a specialist, to undergo appropriate therapy. What is the treatment for varicose veins on the lower leg? What are their advantages and disadvantages?
Ways to get rid of the disease
Thousands of people every year ask themselves: how to get rid of "ugly knots" or "vascular nets" in their legs? The media portal is full of ads for public and private clinics that treat varicose veins on the lower legs. They offer "unique", "guaranteed", "painless" or "completely safe" ways to get rid of the disease. Sometimes it is difficult to understand these advertisements, to answer the question of which treatment option is most appropriate. If a person has decided to address his enlargement canal and he is unsure about the safety or effectiveness of this method or that method of treatment, the best option for him is to contact several clinics, to seek qualified advice from at least two professionals.
There are various reasons to force patients with varicose veins to see a doctor:
- cosmetic considerations;
- symptoms of discomfort;
- complications of the disease (for example, ulcers, bleeding, or thrombophlebitis);
- fear for your health (how this disease will happen in the future if left untreated).
Sometimes, it is difficult for a doctor to know what a patient wants. Therefore, during the consultation, it is important to seek understanding with the doctor, to convey the main reasons for contacting him properly. Often, patients just need reassurance that their enlarged veins will not harm them in any way and are unlikely to do so in the future.
If there is a need for therapy, doctors often recommend undergoing self -treatment at home within 6 months, which includes:
- the use of compression gowns;
- exercise regularly;
- avoid "long stops" - excluding long stays in a sitting or standing position;
- while resting (in a horizontal position), lift the "compromised" limb above heart level.
If, after a second consultation, the patient is not satisfied with the result, the doctor may recommend conservative treatment or surgery for the varicose veins on the lower leg.
Treatment options for lower limb pathology
To combat leg varicose veins, conservative treatments are used (compression therapy and pharmacology, lifestyle modifications), surgical interventions, external and internal laser exposure, radio frequency ablation, injection sclerotherapy. The choice of this option or options depends on the patient’s preferences. It is also influenced by the financial capability of the patient, the qualifications of the doctor and the equipment of the medical institution. Even so, which method of treating varicose veins in the lower leg will be used in each particular case depends on the disease itself: what symptoms are present, the degree of venous insufficiency and other features of the vascular lesion.
Conservative methods of therapy
Conservative treatment, as a rule, is complex and includes several components.
Lifestyle changes, which imply a complex of measures aimed at preventing blood stasis in the veins. As you know, prolonged standing or sitting position flattens the pump activity of the venous muscle (gastrocnemius muscle), which contributes to stagnation. Therefore, patients are recommended to walk regularly, raising the legs periodically above the level of the heart in a cartilage state. You should also pay attention to a variety of diets - no salt, low in calories. They will allow you to adjust your weight, making up for seasonal vitamin deficiencies. It is necessary to consume foods high in bioflavonoids (substances that help strengthen vessel walls).
People with varicose veins should avoid overheating the feet, refrain from visiting baths and saunas, and, if possible, not use heated floors.
Compression stockings improve venous hemodynamics, which leads to the disappearance of many manifestations of the disease. Disadvantages of this method:
- its use in a limited time (there is no possibility of wearing stockings and compression stockings all the time);
- the appearance of discomfort with constant compression, this is often observed in the summer, when the symptoms of varicose veins most "manifest themselves".
Pharmacies, as a rule, offer compression socks from one manufacturer only. However, there are many different brands, each of which can meet the needs of patients to varying degrees.
Drug treatment can eliminate the symptoms of the disease or reduce their manifestations, aims to prevent and combat its complications, and can increase the effectiveness of compression therapy. Pharmacology helps to overcome the side effects that occur after sclerotherapy or phlebectomy.
Modern treatment of varicose veins in the lower extremities is incomplete without the use of venotonics (phleboprotectors), drugs that can improve symptoms, strengthen the walls of the veins. They are considered basic pharmacotherapeutic agents. This includes:
- Horse chestnut fruit extract and thiamine (vitamin B1) are some of the medications used to treat pain and heaviness in the legs, edema observed in chronic venous insufficiency. The fund has shown its effectiveness in clinical trials. There are dosage forms: oral solution (10-15 drops 3 times a day) and tablet form (usually taken after eating 1 tablet 3 times a day).
- Meat brooms (meat brooms) are used as food additives. Helps relieve congestion in the veins. It is believed to be effective against spider veins. However, clinical data confirming its safety and efficacy have not been performed.
- Deproteinated calf blood hemoderivatives are part of a popular drug, which are excellent phleboprotectors, have a good therapeutic effect for varicose veins on the lower legs.
As a rule, venotonics are prescribed in the course. The duration of the course depends on the dynamics of symptom improvement, the duration of remission achieved. Therefore, doctors can change the medication intake from 3 to 6 months or more.
Ointments and gels (topical medications) are also widely used. The treatment regimen for varicose veins in the lower part of the leg is chosen by the doctor depending on the condition and course of the disease. The therapeutic effects of these topical medications are realized through two mechanisms: interfering and in fact therapeutic. Initially, evaporation of the alcohol base or essential oil contained in the gel occurs, which causes a decrease in skin temperature, respectively, and improves the symptoms of the disease. As a result of the latter, the drug substance that penetrates the skin directly into the veins begins to have its therapeutic effect.
Ointments and gels used for leg varicose veins are classified according to the main active ingredients they contain. They include medical materials such as:
- Phleboprotectors (usually routine, as well as plant materials that strengthen vessel walls).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used to relieve pain.
- Topical corticosteroids are used for allergic dermatitis, which can occur as a complication of venous insufficiency.
- H1-histamine receptor blockers are prescribed instead of corticosteroids when the latter is contraindicated.
- Protein enzymes can effectively clear trophic ulcers (complications of distant leg varicose veins).
- Ionized silver is an effective antiseptic, cleanses and dries wounds perfectly, therefore it is an indispensable remedy for the treatment of infected trophic ulcers.
- Antibiotics are used topically for infections of varicose vein complications (thrombophlebitis, dermatitis).
- Restorative preparations and dermatoprotectors protect the skin from external influences, increase its elasticity. They are usually prescribed for atrophic skin changes (when compression stockings are used for a long time).
- Heparin, in addition to antithrombotic activity (prevents the formation of blood clots), has anti-inflammatory effects, able to relieve pain.
Surgery
The main goal of surgical treatment is to eliminate the pathological mechanism that causes the emergence of the disease - venous reflex, as well as to eliminate its main manifestation - varicose veins. Surgical treatment is indicated: for patients with persistent pain and fatigue in the legs, in the presence of edema, chronic venous insufficiency, cosmetic problems, early hyperpigmentation (excessive pigment deposition on the skin), external bleeding, as well as when superficial thrombophlebitis occurs, in the presence of ulcerstrophic that cannot be treated with conservative methods.
Currently, the most popular are three types of operations:
- sapheno-femoral ligation (ligation and removal of the upper part of the great saphenous vein);
- great saphenous vein disposal:
- traditional surgery or Bebkokk, in which a special probe is inserted into the lumen of the great saphenous vein (two incisions are made initially: one in the groin area, the second at the level of the upper third of the leg) and extended along the entire length, then removed along with the varicose veins;
- cryostripping, an operation almost similar to the previous one, but different in that the probe is cooled to -85 ° C, as a result of which the vein adheres to the probe, which makes it possible to remove it less trauma;
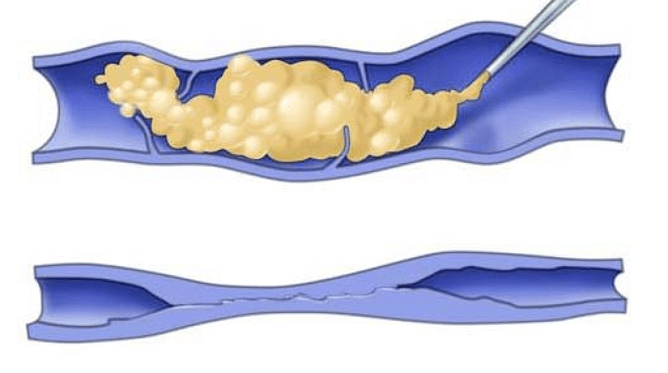
- Phlebectomy is a procedure to remove varicose veins through several small incisions of 2-3 mm in the skin.
The above surgical interventions help improve the patient’s quality of life; their therapeutic and economic efficacy have been proven in clinical trials. They are usually performed under general anesthesia, but most patients are removed on the day of surgery. Full recovery, returning to normal daily activities usually takes 2 to 3 weeks. Complications may occur, which are more common in patients with advanced varicose veins. During surgery, nerves located in the subcutaneous tissue can be damaged, therefore, after surgical manipulation, temporary numbness or even some parts of the leg are sometimes observed, but this does not cause serious deformity.
New treatment
The main goal of using the new treatment method is to minimize the tissue trauma observed during the surgical intervention, allowing the patient to recover more quickly. They began to be widely used in the early 2000s.
Intravenous ablation (RF and laser)
Radio frequency and laser ablation are methods of treating leg varicose veins by "sealing" the large (or small) saphenous vein with high temperature, which causes the backwardness of the dilated duct (its walls sticking together). Although this option does not involve a surgical procedure, it is quite common to use phlebectomy and additional sclerotherapy. Both methods involve:
- Insert the catheter into the great saphenous vein through a small incision in the upper third of the leg and advance it to the saphenofemoral junction under ultrasound guidance. No incisions were made in the groin area.
- Implementation under local anesthesia (anesthetic penetrates widely into the subcutaneous tissue of the thigh). Additional general anesthesia may be required if a large number of miniflebectomies are performed at the same time.
- The need to use a bandage or stockings after the procedure for two weeks.
- The dependence of the result on the anatomy of the saphenous vein in the patient is positive when there is a straight line, doubtful when the vessel is perforated.
The use of intravenous ablation, which has been widely used for the past ten years, shows no significant difference in its effectiveness compared with surgery.
The main advantage of this technique is rapid recovery after the procedure, which is associated with a lower likelihood of wound infection and the incidence of hematomas.
Even so, complications are typical for this procedure: skin burns, temporary paresthesia, deep vein thrombosis (occurring in less than 1% of patients).
Simple sclerotherapy
This method of treatment, due to its ease of implementation and low trauma, is currently used by many clinics. The point lies in the fact that the sclerosant is injected into the varicose veins, the material that attaches to its walls, the blood flow moves to healthy channels. Sclerotherapy is often combined with classical surgery, and in the case of telangiectasia and spider veins, it is used as the only method of therapy.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy,
- breastfeeding period,
- dermatitis,
- thrombophlebitis.
Sclerotherapy provides acceptable results that satisfy many patients.
Sclerotherapy foam
Unlike simple sclerotherapy, with foam, sclerosant is injected into a vein after mixing it with gas (usually air). As a result, foam is obtained, which, spreading through the veins, diverts blood from it and causes vessel spasm. Usually the manipulation is performed under the guidance of duplex ultrasound scanning.
As well as simple foam sclerotherapy, he is required to wear compression socks after manipulation for 14 days.
Recovery after the procedure is faster than if classical surgery was performed. However, the outcome of medium -term treatment (possible recurrent reflux) of foam sclerotherapy is somewhat worse than that of surgery.
Treatment of "microvaricose": telangiectasia, spider veins
Treatment of spider veins is almost always done for cosmetic reasons only, although it can sometimes cause a hot and throbbing sensation, which indicates the presence of reflux. Usually two types of therapy are used:
- Microsclerotherapy - the introduction of sclerosing material using a thin needle. Usually several spider veins are closed at the same time. Compression bandages or stockings are used for 1 to 2 days. If sclerosis comes out of the vessel during the injection, ulceration can develop in this area, which heals slowly, after which the scar remains. This is rare, provided "if the doctor’s hand does not shake during the operation. " Hyperpigmentation at the injection site (darkening of the skin) is also possible.
- Laser removal. This method works well for treating telangiectasias (intradermal vascular growths that look like birthmarks).
There are many effective methods to get rid of varicose veins from the lower part of the legs offered by traditional medicine. The choice of treatment option is highly dependent on the patient’s own decision. Do not immediately "go under the knife", in the doctor's warehouse there are effective options for conservative therapy. According to doctors, today it is impossible to cure the disease completely, but there is indeed the power of modern medicine to save patients from the manifestations of the disease as much as possible and prevent its further development.




































