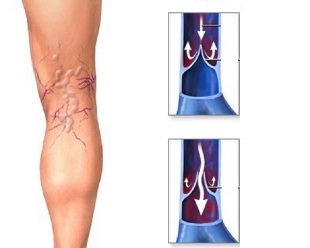
Varicose veins (varicose veins) is one of the most common and oldest diseases of the circulatory system, which has opened up since the times of ancient Egypt. With the help of the egyptian papyri and of the excavation, was found a mummy with signs of varicose veins. This disease is concerned, and that famous ancient doctors: Hippocrates, Galen, Avicenna, and later Troyanova, Trendelenburg. Happening now is the disease has not lost its importance in modern medicine. The definition of "Varicose" comes from the Latin word "d", which means "extension", therefore, the disease received the name "Varicose veins". This disease is characterized by one and the increased length in the peripheral vein in the form of a serpentine tortuosity (deformations), as well as a violation of the flow of blood to it, resulting from failure valve apparatus and the weakening of its wall. The disease most commonly affects the veins of the lower limbs, as well as the main load of the output of blood (large volume), that represent exactly of them, so preference is given to this section. Varicose veins occurs in about 17 to 25% of the population. From early on, the disease is also found that the young men and young women. In the middle age of a woman patients, in 2 to 3 times more prone than men due to the hormonal adaptation of the female body (menstruation, pregnancy, menopause).
Causes and risk factors for the development of varicose veins
The exact cause of the disease is unknown, we only know that, under the influence of some factors develops the weakening of the valves, the pressure increase and loss of elasticity of the wall surface, and a tangle of veins. Risk factors:
- Genetic predisposition: the transfer of the varicose veins by inheritance occurs as a result of a mutation of the gene responsible for the construction of the wall of the vessel, as a result of a mutation the children are born with innate weakness of the connective or muscular tissue of the wall of the vessel, or the disadvantage of their valves (the amount), and as a result occurs the weakness of the vessel wall and increased pressure in the veins.
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause): when the pregnancy changes the hormonal composition of the body (increased levels of progesterone and reduced estrogen), which affect the formation of blood clotting factors (increase), decrease in the tonus of the venous wall (as a result of the destruction of collagen and elastic fibers of the vessel wall), all of this leads to the formation of clots, obstruction of blood vessels and their deformation.
- Obesity : excess weight leads to a sedentary lifestyle, as a result of which the deceleration of blood circulation, in addition to excess fat, increases intra-abdominal pressure, which violates the output of the blood in your veins, resulting in that develops from the venous stasis and the possibility of the development of the disease.
- Diabetes mellitus :a chronic of high levels of sugar in the blood, with time, damages the walls of blood vessels, which is a good medium for the development of a blood clot.
- Alcohol abuse : excessive alcohol consumption leads to dehydration of the body and the thickening of the blood, resulting in forming clots that obstruct vienna and violate the blood outflow.
- The lifting of weights (the porters),a long journey of long years, or stagnant labour (sellers, jigs): is related with the decrease of the muscle tone, increased intra-abdominal pressure and, consequently, the deceleration and the difficulty of the blood flow to the heart and to the development of stagnation in the lower limbs.
- Defects blood clotting disorders: innate hypercoagulation (excess production of factors collapsible blood) leads to the formation of blood clots and cause the promotion of blood through the blood vessels.
- Irrational supply: the lack of some vitamins in the food (vit.Com a, S, P, plant fibres play a role in the reinforcement of the wall of the vessels and improve circulation).
- Wearing close clothing: permanent it wearing takes the machine from compression of the veins, which causes the obstruction of the venous turnover of the lower limbs.
- Chronic constipation : frequent increase of the intra-abdominal pressure (during exertion) leads to the difficulty of blood outflow from the lower limbs.
- Frequent walking, high jump: insufficient movement of the muscles of the leg and the development of stagnation.
- The hottest time of the year: frequent thirst result, dehydration occurs and the sedimentation of the blood and formation of blood clots.
- Clerk of cardiovascular disease or renal disease: is broken the output of venous blood (insufficiency of the heart valves, birth defects).
- Overdose of drugs, promote the coagulation of the blood: the risk of formation of blood clots and occlusion.
- Surgical interventions:the loss of some volume of blood, it is not comfortable position on the operating table (compressing some of the blood vessels), which lead to the risk of occurrence of blood clots.
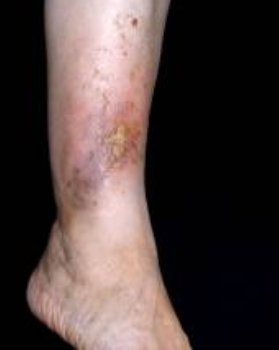
Complications of varicose veins
- The formation of blood clots, resulting in stagnation of blood in the veins;
- the detachment of a blood clot and occlusion of the vessel coincides with its diameter;and
- thrombophlebitis (due to the formation of a blood clot in the lumen of the vein occurs the inflammation of your wall).
- pulmonary embolism (cut off by a clot in the bloodstream falls in the pulmonary artery, which is involved in the movement of a small circle. If the diameter of a blood clot coincides with the diameter of the trunk of this artery, can occur sudden death. If a blood clot smaller than the diameter, it goes further in the branch of the pulmonary artery, causing myocardial easy, or swelling).
- trophic ulcer or eczema feet, in consequence of the violation of power supply (poor circulation of blood leads to a lack of oxygenation in the tissue, which is the most important energy to the tissues of the body);
- swelling of different areas of the body resulting from the stagnation in your veins (they are soft, stretchy, cyanotic color, your education does not depend on the time of day, are often trained in the area of the affected area);
- dermatitis (inflammation of the skin in the affected area), due to violation of the power of this stage;
- the change of color of the skin in the area affected area;
- the seal of subcutaneous fat, the fat in the region of the affected area for account swelling.
The diagnosis of varicose veins
- The flagellum (functionality) testing-definition of patency of the vein and the state of its valves): Troyanova - Trendelenburg,Pratt, Shania, Delbe-. and others. One of the most common experimentation Troyanova - Trendelenburg the patient, when in the horizontal position, lift the leg 45 0, the doctor is stroking the outside of the foot to the top (making that emptied surface of vienna), and then makes the wiring harness to the upper part of the thigh and asks the patient to embark on, the rate of filling of the leg veins must occur more than 15 seconds;
- The ultrasound duplex veins (ultrasound angioscanning) the most informative method allows to evaluate blood flow in the vessel, and to see the vase.
- Dopplerhophy - the method, with which it is estimated is only the blood flow in this vessel;
- Phlebography - the introduction of contrast media intravenously, and the study of x-rays of the painting;
- Phleboscintigraphy - intravenous administration radiopharmaceutical and surveillance in the special device.
Treatment of varicose veins
Nonsurgical treatment

- Popular methods of treatment (as a complement to medical treatment): use compression knitted fabrics (socks); special physical exercises (swimming, biking, skiing, the feet above the head of approximately 20 0 in relation to the bed, a special facility ("bicycle" - lying on his back, and just breathe, imagine that you ride the bike; alternately, fold, and drop of the foot at the ankle joint for the front and back) are applied to improve the output of blood, but only in complicated cases do not); contrast showers (under the jet of water to keep the feet, gradually reducing the temperature of the water reaching the cold); anklets trays (not hot) broth of oak bark, chestnut, chamomile, st. john's; rubbing alcohol infusion of the flowers of acacia, the leaves of Kalanchoe, apple cider vinegar; thrombophlebitis treatment of the infestation of leeches.
- The routine of the day: in the morning, the slow increase of the bed (approximately 5 to 10 minutes), during sleep insert pieces of a cushion under the heel to elevate the foot in about 15 to 20 0 relative to bed, the walk must be calm, it is not possible to sit crossed the foot on the leg, connect the feet elastic bandage from the foot up to the top of the hip, wearing medical stocking, balanced diet, to avoid the tedious movements and of any substances or factors which promote the thickening of the blood, elimination of smoking, warning of constipation.
- Diet : the body is required products that contain vitamins to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve the blood circulation: vitamin c (contained, with citruses, tomatoes, rosehips, and Dr.), vitamin E (beans, liver, egg yolk, green onion), vitamin P (grapefruit, walnut, currant), bioflavonoids (dark cherries, sour cherry), copper (seafood). Sufficient daily amount of liquids, at least 1.5 liters. Limited to the use of alcoholic beverages, coffee, marinated, smoked.
Surgical treatment
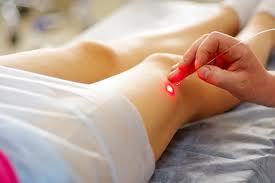
Phlebectomy:Indications for the removal of the veins: an extensive varicose veins, subcutaneous vienna pathologically enlarged, trophic violation of the skin that is not amenable to conservative treatment, acute venous thrombosis, varicose veins extension of the vein is accompanied by a violation of the general condition (expresses tiredness, swelling of the feet) of the patient. Contra-indications to the removal of the veins: coronary artery disease, heavy infectious processes, and the old age of the patient, pregnancy in 2 and 3 quarters, inflammatory processes in the legs (erysipelas inflammation, pyoderma, eczema). The advantages of the surgical treatment: the only form of treatment in cases of a single radical, the method of correction of valves in the deep veins. Disadvantages of surgical treatment: traumatic (cosmetic defect), which requires anesthesia, has several days of hospitalization under the supervision of the surgeon. Laser therapy (endovascular microtermocoagulation) :Indications: the Combination of varicose veins with the following diseases: diseases of the cardiovascular system (ischemic heart disease, increased blood pressure), peripheral vascular disease (phlebitis, thrombophlebitis), respiratory diseases (asthma, bronchitis, pleural effusion), digestive system disorders (cholecystitis, peptic ulcer disease gastric and duodenal), with diseases of nervous system injury (brain injuries, neuroinfections), with diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, endometritis, salpingitis), with skin diseases (dermatitis, Neurodermatitis), peritonitis, boils. Contra-indications: people who suffer from cancer, diseases of the liver, of the kidneys and of the heart in the phase of decompensation, sclerosis of the brain, the pregnancy. Advantages: allows you to get rid of the nasty vascular image, quick procedure (15 to 20minutes), hospitalization is not required, safe and painless, not to hurt the vessel tissue and the surrounding tissues. Disadvantages: it is not in any place available a method expensive method when removing more large vessels possible thermal damage of the fabric that it is possible the formation of scars and depigmentation (clarification) of the skin in areas of impact. The coagulation (ablation) of varicose veins: Indications: varicose veins with a lesion of the trunk of large and small subcutaneous vienna, trophic ulcer due to varicose veins. Contra-indications: sharp thrombophlebitis of the portal vein, the impossibility of active foot, pregnancy, mental disorders. Advantages: without blemish cosmetic, painless, requires no hospitalization, does not violate the work. Disadvantages: the only disadvantage is the price of the procedure. Sclerotherapy: Indications: lower vein varicose, varicose veins great when you use duplex dopplerography, varicose veins in the early stages (if the damage is only to the surface of the veins. Contra-indications: pregnancy and lactation, allergy to sclerosus, deep venous thrombosis, suppurative-inflammatory diseases of the feet. Advantages: lower cost, in comparison with the operation, the rapid period of restoration, you do not need to be in hospital (you can go immediately to the house), the best cosmetic result. Disadvantages:possible to enter the deepest of vienna sclerosus, the efficiency decreases due to a mixture of sclerosus with the blood, it is ineffective in advanced cases.




































